My Senior Year Project, Autonomous Water Surveillance Rover
- Nirav Shah
- Jan 18, 2025
- 2 min read
Updated: Mar 3, 2025
The best way to describe this project is probably pasting Abstract and Conclusion of our college report. Or watch a video at the very end for system architecture explanation. Or downloading our published chapter in Springer below the video.
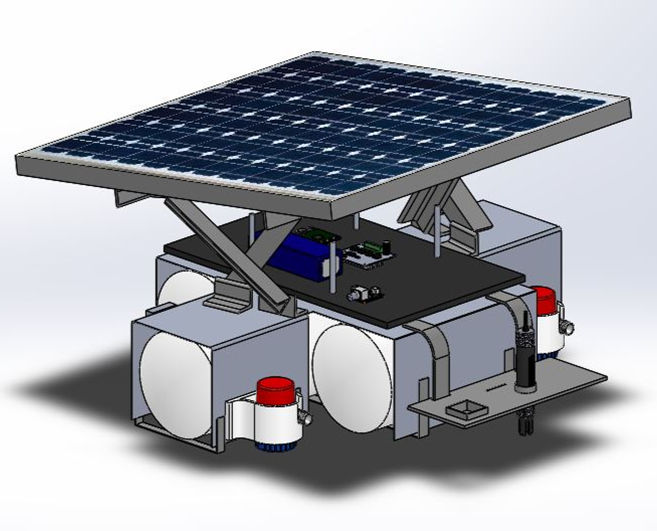
Water pollution is an age-old problem. Effective technologies and regulations to counter this are still under research with booming rate. However, to solve a problem, identification and localization of the root source is essential. Today, to recognize the lakes or any other water bodies dipping over the safety limits, manual methods are employed. Stationary ground stations with sondes immersed at a fixed point are used to measure the water parameters.
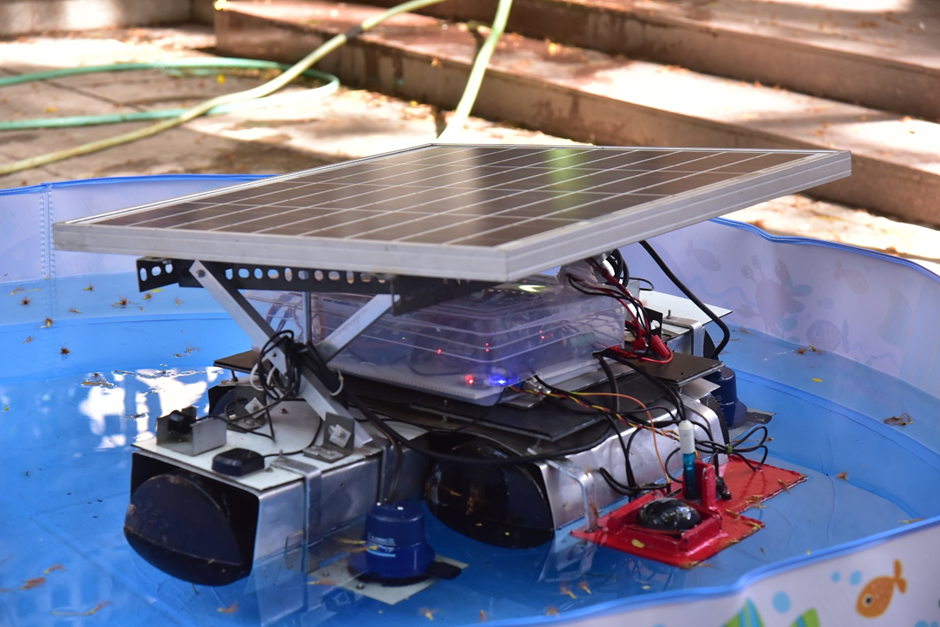
The Autonomous Water Rover monitors a water body by following the path specified by the user using GPS coordinates and traverses the water body as per the instructions with obstacle avoidance. It has different sensors like pH, percentage of dissolved oxygen, temperature, and turbidity. which gives us real time data on our server about the different parameters of the water body. A sonar transducer is also used to provide depth information up to 900 feet. The depth information of a water body can be used by ports, dredging companies and hydrographic offices. The rover also has a camera with first person view which can stream live video to a website in case of any emergencies regarding the waters or on rover itself. An AWR is helpful as it will autonomously do some specified tasks which at present are carried out by humans.
We tested our Autonomous Water Rover at multiple locations, first at Mini Seashore, Vashi, Navi Mumbai, then at Teen Talav, Chembur and also at Neelkanth Housing Society, Vidyavihar East for testing and modification purposes. While testing in the swimming pool, we were assured of its capability of traversing water bodies using differential propulsion and manual control. Autonomous mode of our rover was tested at Mini Seashore as the water pond was very much similar to the conditions of a lake. Also, the area was larger, GPS coordinates assigned could be accurately interpreted by the rover. The sensor data was collected and displayed live on the dedicated webpage. Front and Underwater videos were displayed live on the website and phone. SONAR accurately determined the depth of Mini Seashore.
Targeted Users:
1. Municipal Corporations
2. Dredging Industry
3. Flood Disaster Relief Teams





Entire system architecture explanation with demo
Download the research paper here.


Comments